前言
OC 中的 weak 属性是怎么实现的,为什么在对象释放后会自动变成 nil?本文对这个问题进行了一点探讨。
环境
mac OS Sierra 10.12.4
objc709
参考答案
搜索后发现runtime 如何实现 weak 属性给出了一个参考答案。
runtime对注册的类, 会进行布局,对于weak对象会放入一个hash表中。 用weak指向的对象内存地址作为key,当此对象的引用计数为0的时候会dealloc,假如weak指向的对象内存地址是a,那么就会以a为键, 在这个weak表中搜索,找到所有以a为键的weak对象,从而设置为nil。
测试
代码
1 |
|
结果
对象的 weak 属性调用 setter 时
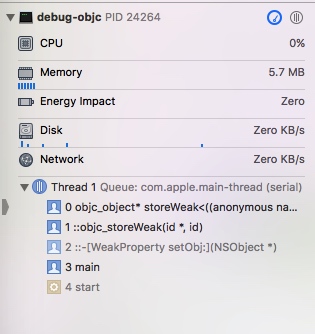
- 调用
id objc_storeWeak(id *location, id newObj) - 调用
static id storeWeak(id *location, objc_object *newObj)
…
使用 NSLog 输出 property.obj 属性时
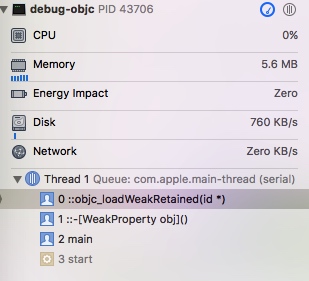
- 调用
id objc_loadWeakRetained(id *location)
当 dealloc 释放对象时
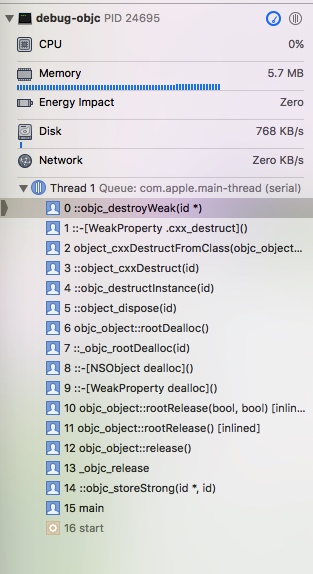
- 调用
void objc_destroyWeak(id *location)
相关函数
查看 NSObject.mm 源码发现
id objc_storeWeak(id *location, id newObj)id objc_storeWeakOrNil(id *location, id newObj)id objc_initWeak(id *location, id newObj)id objc_initWeakOrNil(id *location, id newObj)void objc_destroyWeak(id *location)
都调用了 static id storeWeak(id *location, objc_object *newObj) , objc_xxxWeakOrNil 多了一点额外的处理,但并不影响整体的理解。而 void objc_destroyWeak(id *location) 在调用 static id storeWeak(id *location, objc_object *newObj) 时 newObj 参数传递的是 nil 这一点与上面提到的参考答案中关于 dealloc 释放对象时,将哈希表中指定的键对应的值设置为 nil 是符合的。
小结
storeWeak函数用于为weak属性赋值 (包括销毁)objc_loadWeakRetained函数用于获取weak属性
观察 & 分析
对于函数 storeWeak 主要分析两种情况下的调用
- 赋值,即
id objc_storeWeak(id *location, id newObj) - 销毁,即
void objc_destroyWeak(id *location)
而对于 weak 属性的获取主要分析
- 函数
id objc_loadWeakRetained(id *location)
观察: id objc_storeWeak(id *location, id newObj)
1 | /** |
该函数单纯的调用了 storeWeak 函数
观察: void objc_destroyWeak(id *location)
1 | /** |
该函数也只是单纯的调用了 storeWeak 函数
函数 storeWeak 源码
1 | template <HaveOld haveOld, HaveNew haveNew, |
可以结合 lldb 边调试边对其进行分析,
分析: id objc_storeWeak(id *location, id newObj)
1 | // Template parameters. |
对于模板参数,传递的是 DoHaveOld(true) & DoHaveNew(true)
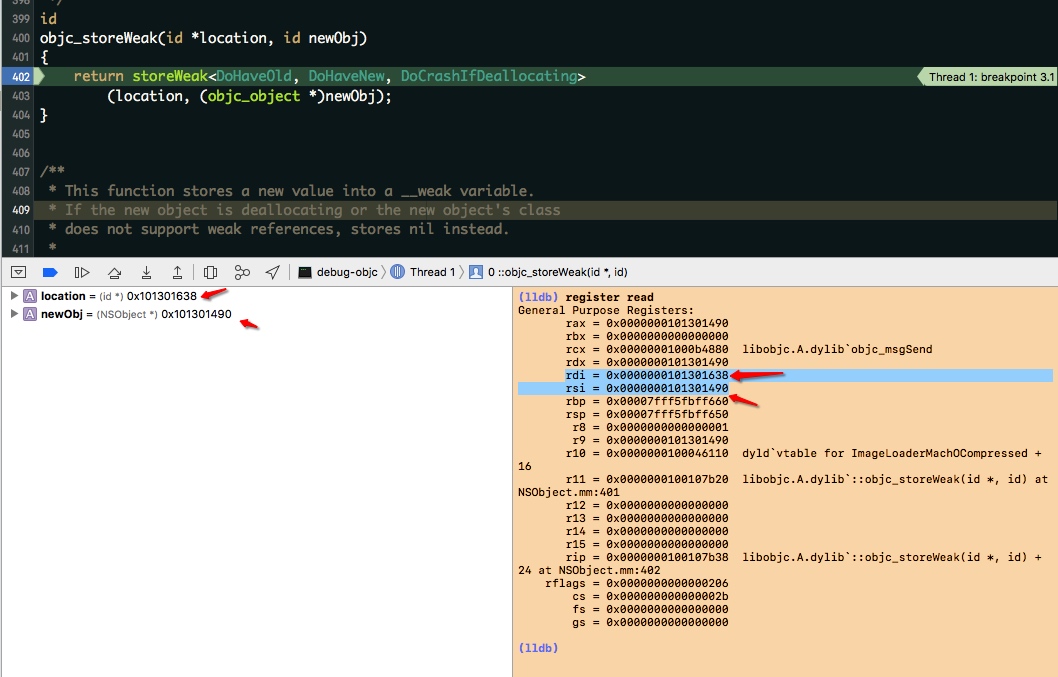
在64位汇编中,当参数少于7个时, 参数从左到右放入寄存器: rdi, rsi, rdx, rcx, r8, r9。此处 location 和 newObj 分别来自 rdi 和 rsi。
根据注释加地址比较,可知 location 为 指向弱引用的地址,newObj 为要求 弱引用指向的地址,在当前场景下为赋值给 WeakProperty 的 obj 属性的 obj 变量。
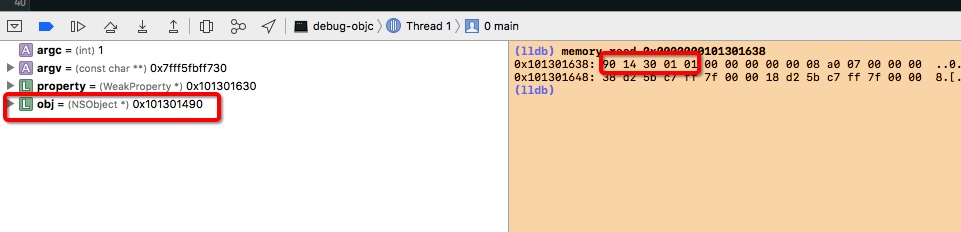
在当前场景下即为执行 storeWeak 后,内存地址 0x0000000101301638 上保存的值为 0x0000000101301490
铺垫: SideTable
关于结构体 SideTable,在本文中当做黑盒来处理
1 | struct SideTable { |
关于 spinlock_t,Wiki 上关于 Spinlock 词条的解释如下
In software engineering, a spinlock is a lock which causes a thread trying to acquire it to simply wait in a loop (“spin”) while repeatedly checking if the lock is available. Since the thread remains active but is not performing a useful task, the use of such a lock is a kind of busy waiting. Once acquired, spinlocks will usually be held until they are explicitly released, although in some implementations they may be automatically released if the thread being waited on (that which holds the lock) blocks, or “goes to sleep.
例子
1 | ; Intel syntax |
配合 google 的翻译可知,自旋锁会循环等待直到锁可用。
从 weak_table_t 结构体的注释说明了,它会保存 ids 和 keys 的形式保存对象
1 | /** |
结构体 SideTable 可看做是一个带加锁功能的集合,其中的元素以键值对的形式存放。
在 ObjC 的入口函数 _objc_init 会调用函数 arr_init 来初始化 SideTableBuf 静态变量
正文: id objc_storeWeak(id *location, id newObj)
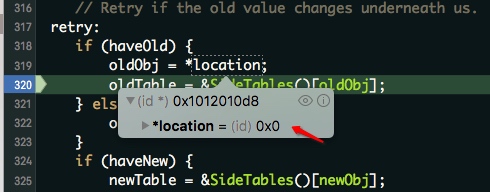
进入 if (haveOld) 条件
创建新元素,因此 location 地址的原值为 nil
进入 SideTables() 函数
1 | static StripedMap<SideTable>& SideTables() { |
reinterpret_cast is the most dangerous cast, and should be used very sparingly. It turns one type directly into another - such as casting the value from one pointer to another, or storing a pointer in an int, or all sorts of other nasty things. Largely, the only guarantee you get with reinterpret_cast is that normally if you cast the result back to the original type, you will get the exact same value (but not if the intermediate type is smaller than the original type). There are a number of conversions that reinterpret_cast cannot do, too. It’s used primarily for particularly weird conversions and bit manipulations, like turning a raw data stream into actual data, or storing data in the low bits of an aligned pointer.
它是一种类型强转的方式
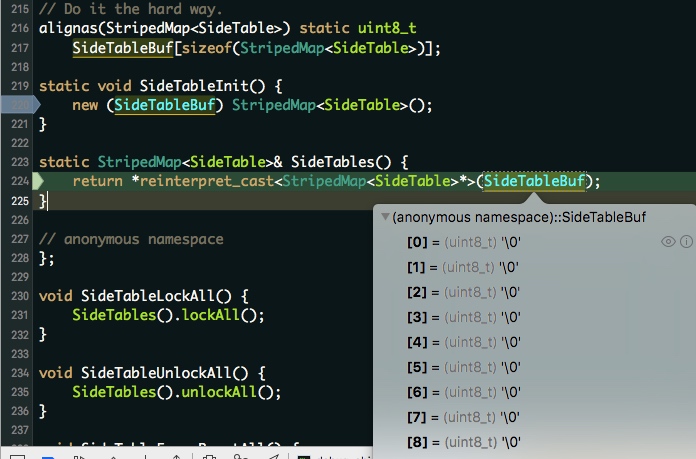
SideTableBuf 是大小为 4096 的 SideTable 缓存数组, oldTable 的赋值相当于在取数组元素,nil 可看成 0 ,即取第一个元素。
同理,haveNew 为 true ,newTable 是以 newObj 为索引在 SideTabBuf 中 查找元素。
调用 SideTable::lockTwo 方法
1 | SideTable::lockTwo<haveOld, haveNew>(oldTable, newTable); |
进入 SideTable::lockTwo 方法
1 | template<> |
进入 lockTwo 方法
1 | // Address-ordered lock discipline for a pair of locks. |
*判断 if (haveOld && location != oldObj) 条件
haveOld && *location != oldObj ,oldObj 被赋值为 *location 正常情况下,两者相等,不等说明出了问题,算是容错。
判断 if (haveNew && newObj) 条件
haveNew && newObj 根据注释可知也是一个容错的处理
清除旧值
1 | if (haveOld) { |
赋予新值
1 | // Assign new value, if any. |
以 location 为 key,以 newObj 为值保存到对应的 weak_table_t 的结构体中
调用 SideTable::unlockTwo 方法
1 | SideTable::unlockTwo<haveOld, haveNew>(oldTable, newTable); |
分析: void objc_destroyWeak(id *location)
因为传递的模板参数为 DontHaveNew ,当释放掉旧值后,不会再进入 if (haveNew) 条件中获得新值。
分析: id objc_loadWeakRetained(id *location)
1 | retry: |
通过 * 取值符号操作 location ,获得弱引用指向的地址。
总结
本文通过对 ObjC 运行时粗略分析,来了解 weak 属性是如何进行存储,使用与释放的。ObjC 的类结构中一个静态的键值对表变量,它保存着对象的弱引用属性,其中的键为指向弱引用的内存地址,值为弱引用,当对象销毁时通过键查表,然后将对应的弱引用从表中移除。
参考